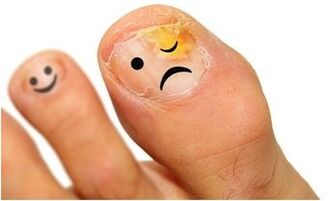
Epidermophytosis of the feet is a group of fungal diseases characterized by damage to the feet, interdigital areas, and nails. It has a high prevalence and is usually observed in people 30 years and older (rarely in children), prone to chronic disease with alternating exacerbations and remissions.
Mycoses are infectious diseases caused by pathogenic or opportunistic fungi. Mushrooms are lower plants without chlorophyll, and ready-made organic matter is necessary for their vital activities - they receive them by depositing on the skin of humans and animals.
The pathogens of fungal infections are very tenacious, which distinguishes them from other microorganisms. Dermatomycosis is the most common disease in the world. Human contact with mushrooms is constant—at home, at work, in the office, in nature, in swimming pools, saunas, and more.
Where can you get fungus?
When you're wearing someone else's shoes, you can get fungus in many public places - bathrooms, saunas, beaches, gyms (especially showers).
If a person does not observe hygiene practices, the risk of infection increases many times over.
symptoms of fungus
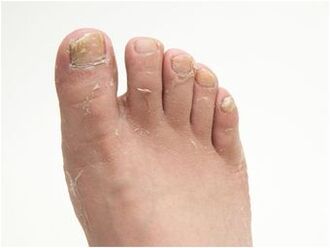
The course and progression of the disease are influenced by the physiology of the foot skin, increased sweating, endocrine system disturbances, and leg injuries. Fungal pathogens can "sleep" for long periods of time without being exposed as symptoms. They can be activated when disturbed in the body. Epidermophytosis of the foot is characterized by the presence of various forms of the disease, which can be complemented by damage to the nail plate.
You can identify the failure of the fungus in the presence of several symptoms:
- The nail plate changes its natural color: yellow or dark is usually set, but the nail can even turn white or completely black;
- Sublamellar keratosis: In appearance, a firm growth appears to appear under the nail;
- Thickening and delamination of sheets;
- Deformation of the nail: it protrudes, grows laterally, grows into the skin;
- Fragility of the nail plate: part of it may chip.
How the disease develops
The initial manifestations of the disease begin in the spaces between the fingers, especially between 4 and 5, as the distance between them is the smallest. There is mild itching at first, and over time a thickened and slightly flaky cuticle develops in the crease of the fingers.
After 2-3 days, a small fissure has formed, from which a slurry is released, which is an excellent medium for the successful reproduction of the fungus. The hard layer of the epidermis may peel off, revealing the dark pink area underneath. Progression of the disease causes it to spread to all fingers and adjacent sides of the foot.
Through damaged areas in the upper part of the skin, the fungus can penetrate deeper behind the epidermis. The disease is accompanied by an eczema reaction. Fluid-filled blisters form on the skin, which are very itchy. Over time, they can combine and erode, resulting in weeping areas.
refer to! When studying fungus-affected skin, it was found that the "bare" wet surfaces that appeared under the air bubbles did not contain the pathogens themselves, but were simply the result of their activity.
If left untreated and properly treated, the fungus can affect the entire surface of the feet and fingers, sometimes reaching the area above the heel. Unstable course - the disease slows down and then gets worse again.
Without treatment, the disease can persist for years. At the same time, the risk of complications from pathogenic streptococci is high: the fluid in the vesicles begins to fester, the inflammatory foci spread beyond the initial border, and the foot swells strongly. A person becomes difficult to move due to leg pain. Also, complications in the form of lymph node problems can occur.
The development of epidermophytosis usually occurs in summer. At this time, sweating increases, the fingers are often wet, and the humidity in the interdigital area increases, creating favorable conditions for the introduction of fungi and their active reproduction.
Mycosis usually appears on 1 and 5 fingers, spreading from the free side. The nails gradually thicken with a yellowish color and uneven sharp edges. Over time, distinct degrees of subungual hyperkeratosis manifested.
Treat foot fungus
For successful treatment, great attention must be paid to the treatment of the lesions.
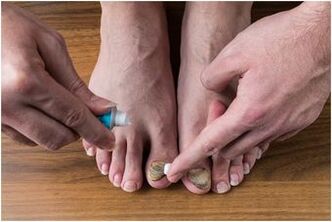
People with fungal infections should soak their feet with potassium permanganate daily. It is necessary to remove the scab, puncture the blister, and remove the "edge" along the eroded area and the border of the ulcerated blister.
After bathing, a medical dressing should be applied to the affected area soaked in an aqueous solution of copper sulfate (0. 1%) and zinc (0. 4%) or a 1% solution of resorcinol. Use an antiseptic-based alcohol solution after the tearing area begins to heal. If necessary, the set is supplemented with antiseptic ointment.
Obtaining the desired results does not depend on the drugs used, but on the correct order of their use according to the current situation of the inflammatory process.
After completing the battle with the lesion, additional treatment makes a huge difference as it helps prevent recurrence. The skin of the feet is wiped with 2% salicyl alcohol or 1% thymol, and 10% boron powder is also required. To remove and prevent fungus from your shoes, you need to wipe from the inside with a formaldehyde solution, then wrap in a dense cloth for a few days, and then dry in fresh air. For socks, tights and stockings, everything is easier - just boil it in this solution for 10 minutes.
Antibiotics are used if there is a pyococcal complication. Be sure to observe bed rest.
prevention
To prevent fungal infections from developing, the following precautions should be taken:
- Owners of swimming pools, gyms, bathrooms should pay more attention to disinfection - thoroughly treat the premises according to the established schedule;
- If a fungal infection is suspected, a doctor should be consulted for immediate interruption of the disease;
- Before going to bed, it is recommended to wash your feet in cold water with soap and dry them thoroughly;
- Do not use other people's shoes;
- Change socks or stockings daily;
- Wear your own shoes when going to the gym's pool, tub, shower.